Shigeyama Sensaku IV (四世茂山千作) passed away at the age of 93. He is one of the greatest Kyōgen actors. Age 93, it’s enough to pass away, but, still very sad. I loved his Kyōgen very much. 合掌.
My thought of gods.#4
I found an interesting article on the Internet. It is Who/what created the world?. On it, Japan has 1,766 votes, 33% of which has polled “God created the world” and 67% of which has polled “Big Bang created the world”.
As soon as I see it, I wonder who is “God”. For people of monotheistic religions, God is the god maybe 100%. But for us? When Japanese poll a vote, how many percents of us imagines “God” monotheists expect? Even if we read the word “God”, in our brain the word is automatically translated into “神”. When it happens, we recognize “God” as “神”. And “神” is never the One God.
Actually, for me, “神 created the world” is consistent with “Big Bang created the world”. Pay attention to the word “神”. It’s never the God. The control room of Hayabusa had an Ofuda of Chūka shrine(中和神社) and others. This is a very famous episode. The Ofuda of Chūka shrine which Dr. Kawaguchi(川口淳一郎) got from the shrine and he made a play on words linking 中和器(chūwa-ki = neutralizer) and 中和神社(Chūka-jinja). They have same kanji characters though their pronunciations are different.
He was not kidding by his act. We have the saying “Do your best and leave the rest to Providence (人事を尽くして天命を待つ)”. He did his best and there was not anything else he could. So, he did make such a play and did pray, I think. Since early times, Japanese have accepted a lot kinds of religions, but we still keep a primitive faith to Nature(自然) in our mind. When we use the word 自然, it also includes us, human-beings.
From the Meiji Restoration(1868) to the end of World War II(1945), Japanese government used Shrines (神社) as one of the tools of state administration, so shrines carry political implications now. But originally, shrines have no relationship with the government. They have long history. In some periods of the long history, they might have some relationship with the powers of the day, but they originated in our primitive faith to Nature.
We have a god everywhere, kitchen oven, bath, lavatory, etc. By the way, bath and lavatory are usually separated in Japan still now.
When Japanese are asked his/her religion, he/she often answers he/she has no religion or he/she is an atheist. You should not blindly accept it. It’s NOT true. It means he/she is not a Christian, not a Muslim, and so on. We, most of Japanese, even today, have our old gods in our mind. It is our religion.
Now, in my garden many kinds of flowers are in bloom. I’ll show you their photos.
And, one of my family loves Ikebana, who picks the flowers from the garden and makes flower arrangements by them in the house. Please take a look!!
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Updating to PHP5.4.15.
Update information Edit(Aug.3)
At May-08 22:51:34UTC, they released PHP5.4.15. However, on May-09, the news read:
“Seriously: PHP 5.4.15 and PHP 5.3.25 really were released!”
- We weren’t trying to pull an April Fool’s Day joke in May. A temporary glitch caused the latest distributions of PHP to not properly propagate to the mirror servers. This has been fixed at the root level, and it’s now being distributed to all of the mirrors. We’ll take some bacon to go with the egg on our faces, please!
- If you continue to experience issues with downloading these versions after 21:00 UTC on 9 May, 2013, please drop us a line at php-mirrors@lists.php.net, telling us from which mirror you’re trying to download, and we’ll get it resolved.
- We apologize for the delays and confusion this may have caused, and thank you for using PHP.
They have had something wrong, haven’t they? Though, I don’t know about it, I’m more interested in ‘We’ll take some bacon to go with the egg on our faces, please!’.
What does the sentence mean exactly? Yes, I can infer the meaning of the sentence from context, though. What is some bacon in the sentence really? This is very difficult for me who is NOT an everyday-English-speaker. Someone, re-write it by using less idiomatic, please, please, please!!!
By the way, I downloaded a Thread Safe version php-5.4.15-Win32-VC9-x86.zip for my server (WindowsXP SP3(x86)).
Acoording to the ChangeLog, it has 7 bug fixes, and upgrades libmagic to 5.14. They say “All users of PHP are encouraged to upgrade to PHP 5.4.14.”.
As php5apache2_4.dll included in the official PHP binary 5.4.10+, I extracted the zip archive and replaced all PHP5.4.13 files with all PHP5.4.14 files except my php.ini. Then, I restarted my Apache. That’s it.
If you need how to configure PHP5.4, please see the post on my Japanese blog. Of course, it is only in Japanese and for a mbstrings user, but I think the information gives some help for you.
Edit(Aug.3):
If you need how to configure PHP5.5, please see “To create a Wamp-like Web Server in Windows7-#2“.
Another information about ~-#4.
I added three new translations to “The translation of Juuni kokuki newsletter by Shinchōsha“.
They show us the two illustrations from “A Thousand Miles of Wind, The Sky at Dawn #1, #2 (風の万里 黎明の空)”.
|
I have a Let’snote, a Panasonic product and a kind of Toughbook, as my mobile PC. Though I configured the dual-boot system of Windows7 and CentOS6, I destroyed all data on the PC before I sent it for repair. When I got it again, I decided to create a Virtual PC and run CentOS6.4 on it. This post is my remainders and I think it gives some convenient for you guys. (^o^)
First, I create a Virtual PC in Windows7 Home Premium on CF-J10TYAHR.
Second, I install CentOS6.4 on the Virtual PC.
|
(Fig.01)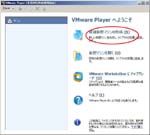 (Fig.02) (Fig.02)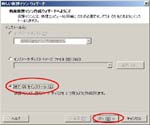 (Fig.03) (Fig.03)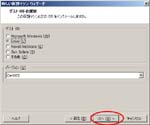 (Fig.04) (Fig.04)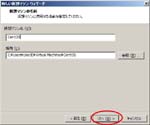 (Fig.05) (Fig.05)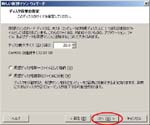 (Fig.06) (Fig.06)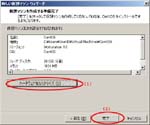 (Fig.07) (Fig.07)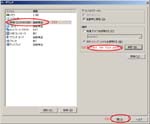 (Fig.08) (Fig.08)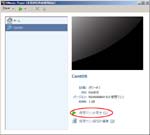 (Fig.09) (Fig.09)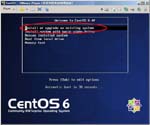 (Fig.10) (Fig.10)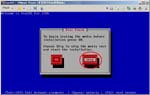 (Fig.11) (Fig.11) (Fig.12) (Fig.12)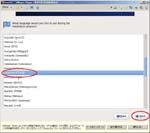 (Fig.13) (Fig.13)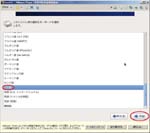 (Fig.14) (Fig.14)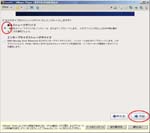 (Fig.15) (Fig.15)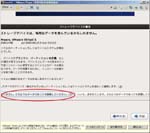 (Fig.16) (Fig.16)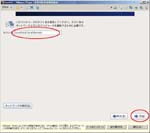 (Fig.17) (Fig.17) (Fig.18) (Fig.18)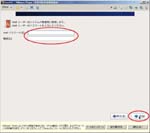 (Fig.19) (Fig.19)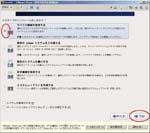 (Fig.20) (Fig.20)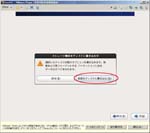 (Fig.21) (Fig.21)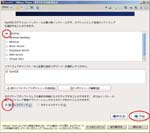 (Fig.22) (Fig.22)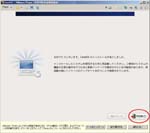 (Fig.23) (Fig.23)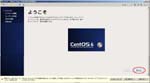 (Fig.24) (Fig.24)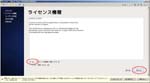 (Fig.25) (Fig.25)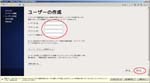 (Fig.26) (Fig.26)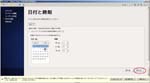 (Fig.27) (Fig.27)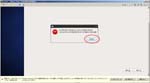 (Fig.28) (Fig.28)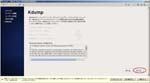 (Fig.29) (Fig.29)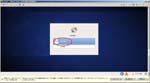 (Fig.30) (Fig.30)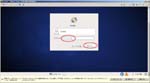 (Fig.31) (Fig.31)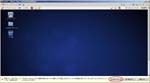 (Fig.32) (Fig.32)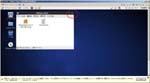 |
As promised in my earlier post, I’m re-translating three short stories, Hisho no Tori (丕緒の鳥), Hyōhaku (漂舶), and Rakushō no Goku (落照の獄).
I’ve finished the re-translation of “Hisho no Tori (丕緒の鳥)”, so, I’ve released my second edition. At this time, I added some phrases forgotten to translate (^^;) and I read my English version by myself again and again before my re-translation. You can find any improvements about this edition, can’t you? I worry about it very much.
By the way, now, I use Prolonged Sound Mark for a long vowel when I romanize some nouns. For example, ō, ū.
Oh! I almost forgot to write. Eugene Woodbury started translating “Tonan no Tsubasa (図南の翼)” on October 18, 2012. You can read it, here.
Updating to MySQL5.6.11 on Windows.
Update information Edit(Apr.28) Edit(May.6)
Today, I’ve updated from MySQL5.6.10 to 5.6.11 on my WindowsXP SP3(x86) server.
- Backup all data.
- Download mysql-5.6.11-win32.zip
- Extract Zip archive.
- Control Panel >> Administrative tools >> Services
Select the MySQL Service name and stop - Overwrite my old installation by the new one.
In my case, I’ve only installed the next things. Of course, I leave my old my.ini in the directory.- directories
bin
data
include
lib
share - file
COPYING
- directories
- Control Panel >> Administrative tools >> Services
Select the MySQL Service name and start
I’ve also updated to phpMyAdmin3.5.8 because of PMASA-2013-1.
Edit(Apr.28):
I updated phpMyAdmin only a week ago, but, according to PMASA-2013-2 and PMASA-2013-3, 3.5.8 has some vulnerabilities, so I’ve updated to 3.5.8.1 today. Ooops!
Edit(May.6):
They released phpMyAdmin 4.0.0 on Fri, 03 May 2013 12:22:50 GMT.
They say,
- Welcome to phpMyAdmin 4.0.0. With this version, the HTML frames are gone and the navigation panel now presents a tree. This version requires Javascript.
- Version 4.0 contains many bug fixes and smaller new features; moreover, the documentation has a new look and contains an index. Enjoy!
Rhododendrons of the mountain.
Today, it’s very sunny. I went and saw blooming rhododendrons to the mountain about which I wrote before, Spring snow, Momijigari(紅葉狩), and Hatsumōde(初詣) five days late. In this season, a garden in the mountain, Hikosan Kaen (英彦山花園), is famous for flowers of rhododendrons (シャクナゲ).
I found the blooming rhododendrons and others in and out of the garden. Beautiful!!
And I also visited Hōheiden (奉幣殿) and got Omikuji. Ha-ha.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Updating to PHP5.4.14.
Update information Edit(Aug.3)
At Apr-10 22:55:28UTC, they released PHP5.4.14. So, I downloaded a Thread Safe version php-5.4.14-Win32-VC9-x86.zip for my server (WindowsXP SP3(x86)).
Acoording to the ChangeLog, it has 11 bug fixes, and merges PCRE 8.32 (released 2012-11-30). This is a security update, so, they say “All users of PHP are encouraged to upgrade to PHP 5.4.14.”.
As php5apache2_4.dll included in the official PHP binary 5.4.10+, I extracted the zip archive and replaced all PHP5.4.13 files with all PHP5.4.14 files except my php.ini. Then, I restarted my Apache. That’s it.
Yeah, that’s it. However, at this time, I inadvertently deleted my php.ini and restarted Apache. So, my WordPress said “Your PHP installation appears to be missing the MySQL extension which is required by WordPress.” when I made this post. (;^_^A アセアセ・・・ We have to be careful not to do this!!!
If you need how to configure PHP5.4, please see the post on my Japanese blog. Of course, it is only in Japanese and for a mbstrings user, but I think the information gives some help for you.
Edit(Aug.3):
If you need how to configure PHP5.5, please see “To create a Wamp-like Web Server in Windows7-#2“.